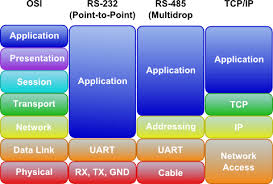
OSI Model
In computer networks, the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a seven-layer structure used to describe the communication process between devices. Each layer provides specific services and functions, which allow devices to communicate across the network.
The following is a brief description of the seven layers of the OSI model:
- Physical Layer: This is the lowest layer of the OSI model, which is responsible for the transmission of data over the physical medium of the network, such as copper or fiber optic cables.
- Data link layer: This layer is responsible for the reliable transfer of data between devices on the same network. It also provides functions for detecting and correcting errors in the transmitted data.
- Network layer: The network layer is responsible for routing data packets across multiple networks. This layer uses logical addresses, such as IP addresses, to identify devices and network paths.
- Transport layer: The transport layer handles the reliable delivery of data between end devices, providing services such as flow control and error correction.
- Session layer: This layer is responsible for establishing and maintaining communication sessions between devices. It also provides session management services such as authentication and authorization.
- Presentation layer: The presentation layer is responsible for data representation, providing functions such as data encoding and decoding, compression and encryption.
- Application layer: The application layer provides services for end-user applications such as email, web browsers and file transfer.